Venous Ulcers
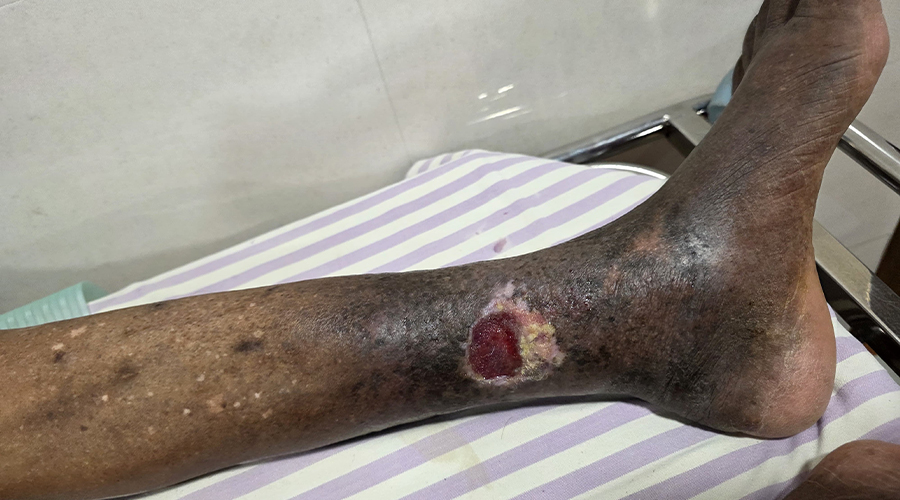
Venous ulcers, the most advanced form of chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), are open lesions between the knee and ankle caused by venous disease.
- They account for 60–80% of leg ulcers, with a prevalence of 1–3% in the general population, increasing with age.
- Risk factors include obesity, immobility, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and venous hypertension due to reflux or obstruction.
- Venous ulcers are typically shallow, irregular, and located near bony prominences, often associated with edema, lipodermatosclerosis, or varicose veins.
Differentiation of leg Ulcers from venous ulcers
| Type | Characteristics | Location | Etiology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Venous | Shallow, irregular edges; edema; hyperpigmentation; associated with varicose veins | Medial malleolus | Venous hypertension/reflux |
| Arterial | Deep, punched-out edges; pale base; cold extremities; diminished pulses | Toes, lateral foot | Arterial insufficiency |
| Neuropathic | Painless; thick callus; undermined edges | Pressure points (e.g., sole) | Diabetes-related neuropathy |
| Vasculitis | Painful; purpuric base; systemic symptoms | Anywhere | Immune-mediated inflammation |
Type: Venous
Characteristics: Shallow, irregular edges; edema; hyperpigmentation; associated with varicose veins
Location: Medial malleolus
Etiology: Venous hypertension/reflux
Type: Arterial
Characteristics: Deep, punched-out edges; pale base; cold extremities; diminished pulses
Location: Toes, lateral foot
Etiology: Arterial insufficiency
Type: Neuropathic
Characteristics: Painless; thick callus; undermined edges
Location: Pressure points (e.g., sole)
Etiology: Diabetes-related neuropathy
Type: Vasculitis
Characteristics: Painful; purpuric base; systemic symptoms
Location: Anywhere
Etiology: Immune-mediated inflammation
Management of Venous Ulcers
Minimally Invasive Therapies
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA): Uses laser energy to close incompetent veins, reducing venous reflux and ulcer recurrence. It is well-tolerated with fewer side effects compared to surgery7.
- Glue Therapy: Cyanoacrylate adhesive seals veins without thermal damage, offering a quick recovery7.
- Sclerotherapy: Injection of sclerosants into veins induces fibrosis and closure, effective for superficial venous disease7.
Topical Applications
- Silver-impregnated dressings enhance short-term healing..
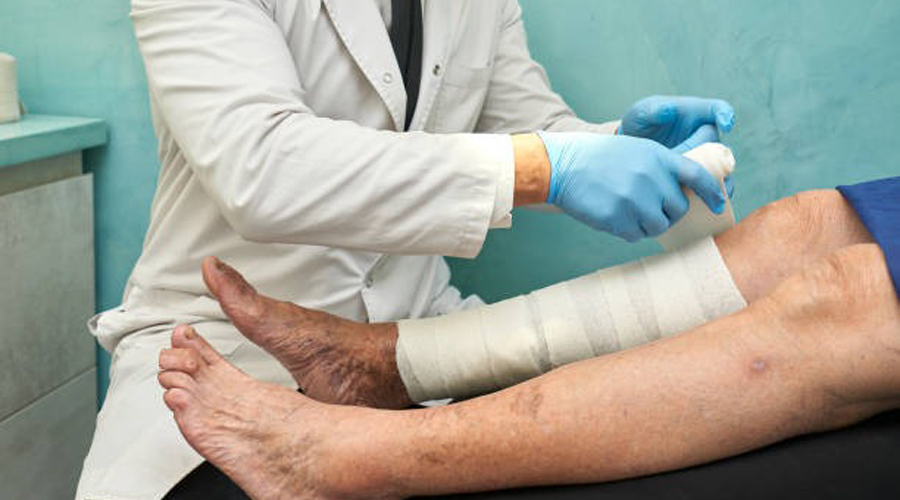
Compression Therapy
Four-layer bandages provide sustained compression to reduce edema and improve venous return, a cornerstone in venous ulcer management.
Citations:
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8615583/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3930479/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5991028/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31478635/
- https://effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/products/venous-ulcers-treatment/research-protocol
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4144244/
- https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2019/0601/p682.html
- https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2019/0901/p298.html
